Index & Interest Rate
Global Products Hotline:(852) 3890 0638
Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average is the oldest market index in the world, created by Charles Dow and Edward Jones in the Wall Street Journal in 1884. There are no specific rules for a company to be included at the beginning and the companies to be included are chosen by the editorial board of the Wall Street Journal since October 1896. In 1928, the components of the Dow were increased to 30 stocks. The Dow Jones Industrial Average is the most popular and widely-recognized stock market index in the world. It is a basket of 30 blue-chip stocks listed on the New York Stock Exchange, which represent more than a fifth of the investable US stock market's value. The futures contracts based on The Dow Jones Industrial Average are provided by the The Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT) exchange for investors in the markets.
Factors affecting prices
1. Interest Rate Policy
2. Current Account
3. Employment Rate
4. Profitability Index for Enterprises
5. Productivity Growth Index
Standard & Poor's 500 Index
The S&P 500 is a capitalization-weighted index with components selected by McGraw Hill from stocks listed on US exchanges such as New York Stock Exchange and American Stock Exchange, including 400 stocks from the industrial sector, 40 from the utilities sector, 40 from the financial sector and 20 from the transportation sector. As S&P 500 captures approximately 80% coverage of available market capitalization in the New York Stock Exchange and the components are selected based on their liquidity, size, and industry, the introduction of S&P 500 caught the eye of institutions and fund managers and it has become one of the most recognized index futures product for investors in the US. The value of the full-sized S&P 500 contract had become too large for most small traders so the Chicago Mercantile Exchange introduced a much related E-mini S&P 500 futures contract in September 9, 1998 and the E-mini made futures trading accessible to more traders. E-mini S&P 500 futures contract tracks the S&P 500 index but, as opposed to normal S&P futures contracts which have a point value of $250, E-mini S&P 500 futures contract has a point value of $50 and are mostly traded by electronic means. Moreover, the principle for adding and deleting constituent stocks is one of the characteristics of S&P 500 as it keeps the number of firms in the S&P 500 constant at 500.
Factors affecting prices
1. Economic Growth
2. Inflation
3. Political Factors
4. Other Factors (e.g. tax break in the US, exchange rate change)
NASDAQ-100 Index
The Nasdaq-100 Index includes 100 of the largest domestic and international non-financial companies listed on The Nasdaq Stock Market (which has around 5400 listed company). The index was designed as a market capitalization-weighted index in 1985 with a base value set to 250 on February 1 of that year. Since the close of trading on December 18, 1998, the NASDAQ-100 Index has been changed to a modified capitalization-weighted index and Nasdaq will review the composition of the Nasdaq-100 Index on a quarterly basis, with stocks classified into large stocks and small stocks, in order to limit the domination of the index by a few large stocks while providing enhanced diversification. The Nasdaq-100 Index is calculated every 15 seconds and it has a high correlation (94%) with the Nasdaq Composite Index with components including world famous, leading corporations of different industries, such as Cisco, Microsoft, Intel, Oracle, QUALCOMM, Sun Microsystems, JDS Uniphase, VERITAS, Siebel, and Amgen.
Factors affecting prices
1. Economic Prospects
2. Movement of US Dollar and Interest Rate
3. Political Factors
4. Prices of Raw Materials
5. Productivity Growth Index
Interest Rate Futures
Bond futures are futures contracts for the contract holder to buy or sell a bond with fixed income while the price will be affected by the change of interest rate. It is a main tool for hedging long-term interest-rate risk. The contract terms for U.S. bond futures go from 2 years to as long as 30 years. There are 2 major risks in interest rate bond futures: interest-rate risk and default risk. Interest-rate risk is sometimes called reinvestment risk; in other words, the price of the bond changes due to the change of interest rate. Default risk occurs when the issuer faces financial distress and fails to make an interest or principal payment. In general, bonds having higher risk will pay a higher yield in order to attract investors.
Factors affecting prices
1. Movement of Interest Rates
2. Influence of Stock Markets
3. Inflation
4. Financial Position of the U.S. Government
SGX CME Nikkei 225 Index
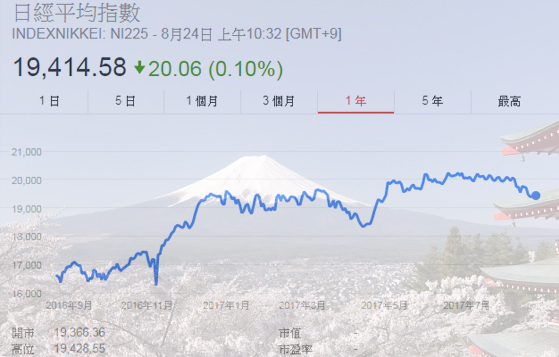
The Nikkei Stock Average Index, formerly the Tokyo Stock Exchange Adjusted Average Stock Price, is compiled and published by Nihon Keizai Shimbun (NKS), representing the price development of the stocks in the Japan market. Nikkei 225 index has been calculated continuously since September 7, 1950 while the 225 components of the Nikkei Stock Average are among the stocks listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange. After more than 50 years of political and economic development, Nikkei 225 index has risen from 176.2 on the first day to over 10,000 as of today. As an index representing Japan stocks, this index is reported by major international quote service providers and used worldwide as the indicator of Japan's economy. Customers can track the overall movement of Japan stock market by trading SGX & CME Nikkei 225 Index.
Factors affecting prices
1. Economic Growth
2. Current Account
3. Productivity Growth Index
4. Movement of International Interest Rates
5. Political Landscape of Nearby Countries
6. Local Factors:
A. Japan's Political Landscape
B. Zero Interest Rate Policy Implemented by Bank of Japan
C. Movement of Japanese Yen's Exchange Rates
SGX FTSE CHINA A50 INDEX FUTURES
SGX FTSE China A50 Index Futures was listed on SGX on 5 September 2006, tracking the performance of the underlying FTSE China A50 Index which was introduced by FTSE, one of four largest index provider in the world. SGX China A50 Index Futures is the world's only offshore futures tracking the A-share market approved by CFTC. It serves the need from QFII for hedging the risk of A-shares as it is composed of the 50 largest companies in mainland China, trading on the Shanghai and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges. Indicators of the index, including the performance, liquidity, volatility, sector exposure and market representation, all reaches a marketing leading standard. The FTSE China A50 Index is a free-float adjusted, liquidity-screened index with a base value of 5,000 points on July 21, 2003. It is reviewed quarterly in March, June, September and December to ensure the index remains representative of the underlying China market. Moreover, FTSE China A50 Index has a strong correlation with CSI 300 index that the top 10 weighted stocks of the indexes are basically the same. The "A" in A50 Index represents A-shares while "50" represents top 50 stocks by total market capitalization. There are diversified participants in the market: investment banks, hedging funds, asset management companies, proprietary trading firms and individual investors.
Factors affecting prices
1. Economic Prospects and Growth in China
2. Inflation and Consumer Price Index of China
3. Political Factors
4. Other Factors (e.g. tax reduction, interest rate trend, Renminbi's exchange rate movement, implementation of different policies)
SGX MSCI Taiwan Index Futures
SGX MSCI Taiwan Index Futures is a free-float adjusted and capitalization-weighted index constituted by large cap, mid cap, and small cap stocks of Taiwan. Since it was introduced in 1997, its trading volume and open interest has grown significantly. The index is approved by CFTC. According to IMF, Taiwan's GDP reached approximately 466.1 USD billion in 2012, ranked 20 in the world. Taiwan's stock market reached a market capitalization of US$808 billion on 1 July 2011. To international institutes and private investors participating in Taiwan's stock market, SGX MSCI Taiwan Index Futures is a multifunctional and cost-effective risk management tool.
Factors affecting prices
1. Current Account
2. Economic Prospects and Growth in Taiwan
3. Inflation and Consumer Price Index of Taiwan
4. Employment Rate
5. Local Political Factors
6. Other Factors (e.g. Taiwan New Dollar's exchange rate movement, China-US-Taiwan relations)
Global Products Hotline






